ConcurrentMap是一個接口並且它是一個成員Java集合框架,在 JDK 1.5 中引入,代表一個 Map,能夠處理對其的並發訪問,而不影響 Map 中條目的一致性。 ConcurrentMap 接口存在於java.util.concurrent包。除了從 SuperInterface 繼承的方法之外,它還提供了一些額外的方法,即Map。它繼承了嵌套接口Map.Entry。
HashMap操作不同步,而哈希表提供同步。雖然Hashtable是線程安全的,但它的效率不是很高。為了解決這個問題,Java Collections Framework 引入了ConcurrentMap在Java 1.5中。
ConcurrentMap的層次結構
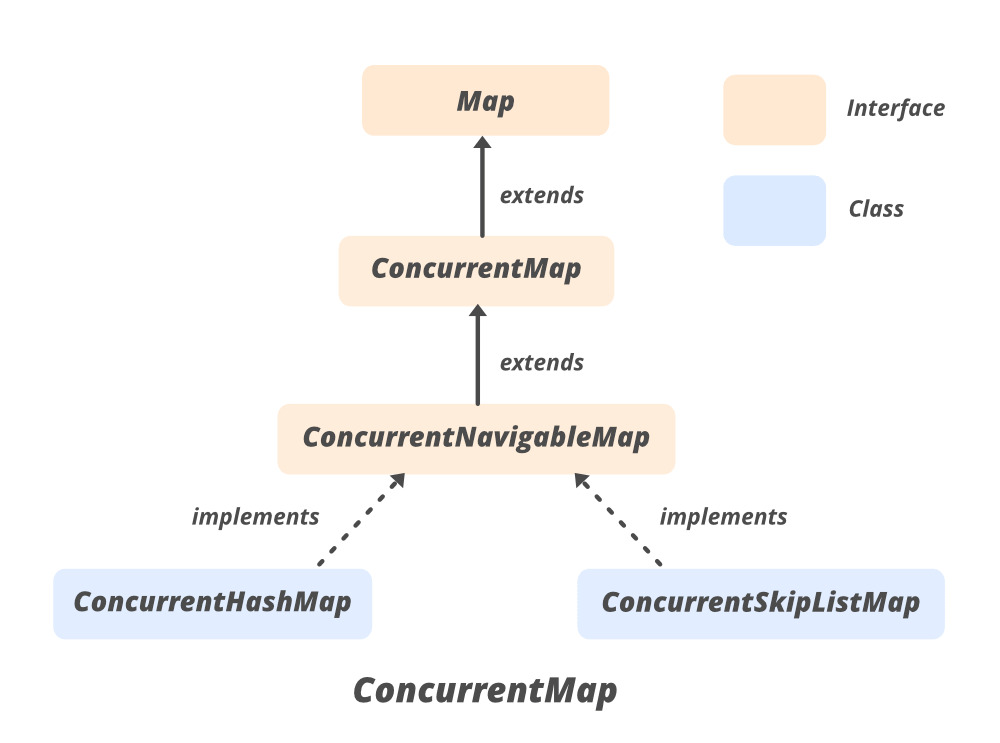
聲明:
public interface ConcurrentMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V>
這裏,K是鍵Object的類型,V是值Object的類型。
- 它擴展了 Map interface in Java 。
- ConcurrentNavigableMap<K,V> 是子接口。
- ConcurrentMap 的實現方式是ConcurrentHashMap,ConcurrentSkipListMap類。
- ConcurrentMap 被稱為同步映射。
實現類
由於它屬於java.util.concurrent包,我們必須導入正在使用
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap
or
import java.util.concurrent.*
ConcurrentMap 有兩個實現類,它們是ConcurrentSkipListMap和ConcurrentHashMap。 ConcurrentSkipListMap 是一個可擴展的實現ConcurrentNavigableMap擴展ConcurrentMap接口的接口。 ConcurrentSkipListMap 中的鍵按自然順序排序或在構造對象時使用比較器排序。 ConcurrentSkipListMap 的預期時間成本為日誌(n)用於插入、刪除和搜索操作。它是一個線程安全的類,因此,所有基本操作都可以並發完成。
用法:
// ConcurrentMap implementation by ConcurrentHashMap CocurrentMap<K, V> numbers = new ConcurrentHashMap<K, V>(); // ConcurrentMap implementation by ConcurrentSkipListMap ConcurrentMap< ? , ? > objectName = new ConcurrentSkipListMap< ? , ? >();
例子:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate methods
// of ConcurrentMap interface
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Since ConcurrentMap is an interface,
// we create instance using ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentMap<Integer, String> m = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String>();
m.put(100, "Geeks");
m.put(101, "For");
m.put(102, "Geeks");
// Here we cant add Hello because 101 key
// is already present
m.putIfAbsent(101, "Hello");
// We can remove entry because 101 key
// is associated with For value
m.remove(101, "For");
// Now we can add Hello
m.putIfAbsent(101, "Hello");
// We can replace Hello with For
m.replace(101, "Hello", "For");
System.out.println("Map contents : " + m);
}
}Map contents : {100=Geeks, 101=For, 102=Geeks}
Basic Methods
1. 添加元素
ConcurrentSkipListMap 的 put() 方法是 Java 中的內置函數,它將指定值與此映射中的指定鍵相關聯。如果映射之前包含鍵的映射,則舊值將被替換。
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate adding
// elements
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentMap
// is an interface so We use
// ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentMap<Integer, Integer> mpp = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, Integer>();
// Adding elements to this map
// using put() method
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
mpp.put(i, i);
// Print map to the console
System.out.println("After put(): " + mpp);
}
}After put(): {1=1, 2=2, 3=3, 4=4, 5=5}
2. 刪除元素
ConcurrentSkipListMap 的 remove() 方法是 Java 中的內置函數,用於從此映射中刪除指定鍵的映射。如果該特定鍵沒有映射,則該方法返回 null。執行此方法後,Map的大小會減小。
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate removing
// elements
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentMap
// is an interface so We use
// ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentMap<Integer, Integer> mpp = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, Integer>();
// Adding elements to this map
// using put method
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
mpp.put(i, i);
// remove() mapping associated
// with key 1
mpp.remove(1);
System.out.println("After remove(): " + mpp);
}
}After remove(): {2=2, 3=3, 4=4, 5=5}
3. 訪問元素
我們可以使用 get() 方法訪問 ConcurrentSkipListMap 的元素,下麵給出了示例。
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate accessing
// elements
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentMap
// is an interface so We use
// ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentMap<Integer, String> chm = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String>();
// insert mappings using put method
chm.put(100, "Geeks");
chm.put(101, "for");
chm.put(102, "Geeks");
chm.put(103, "Contribute");
// Displaying the HashMap
System.out.println("The Mappings are: ");
System.out.println(chm);
// Display the value of 100
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "100 is : " + chm.get(100));
// Getting the value of 103
System.out.println("The Value associated to "
+ "103 is : " + chm.get(103));
}
}The Mappings are:
{100=Geeks, 101=for, 102=Geeks, 103=Contribute}
The Value associated to 100 is : Geeks
The Value associated to 103 is : Contribute
4. 遍曆
我們可以使用 Iterator 接口來遍曆 Collection Framework 的任何結構。由於迭代器使用一種類型的數據,因此我們使用 Entry< ? , ? > 將兩種不同的類型解析為兼容的格式。然後使用 next() 方法打印 ConcurrentSkipListMap 的元素。
Java
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TraversingExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentMap
// is an interface so We use
// ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentMap<Integer, String> chmap = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<Integer, String>();
// Add elements using put()
chmap.put(8, "Third");
chmap.put(6, "Second");
chmap.put(3, "First");
chmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Create an Iterator over the
// ConcurrentSkipListMap
Iterator<ConcurrentSkipListMap
.Entry<Integer, String> > itr
= chmap.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
ConcurrentSkipListMap
.Entry<Integer, String> entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}Key = 3, Value = First Key = 6, Value = Second Key = 8, Value = Third Key = 11, Value = Fourth
ConcurrentMap的方法
- K- Map中按鍵的類型。
- V- 映射中映射的值的類型。
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
|
計算(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,?擴展 V> 重映射函數) |
嘗試計算指定鍵及其當前映射值的映射(如果沒有當前映射,則為 null)。 |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? 擴展 V> 映射函數) | 如果指定的鍵尚未與值關聯(或映射為 null),則嘗試使用給定的映射函數計算其值並將其輸入到此映射中,除非 null。 |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定鍵的值存在且非空,則嘗試在給定鍵及其當前映射值的情況下計算新映射。 |
| forEach(BiConsumer<?超級 K,?超級 V> 操作) | 對此映射中的每個條目執行給定的操作,直到處理完所有條目或該操作引發異常。 |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 返回指定鍵映射到的值,如果此映射不包含該鍵的映射,則返回 defaultValue。 |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | 如果指定的鍵尚未與值關聯或與 null 關聯,則將其與給定的非 null 值關聯。 |
| putIfAbsent(K 鍵, V 值) | 如果指定的鍵尚未與值關聯,則將其與給定值關聯。 |
| 刪除(對象鍵,對象值) | 僅當當前映射到給定值時才刪除鍵的條目。 |
| 替換(K鍵,V值) | 僅當當前映射到某個值時才替換鍵的條目。 |
| 替換(K 鍵,V 舊值,V 新值) | 僅當當前映射到給定值時才替換鍵的條目。 |
| ReplaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? 擴展 V> 函數) | 將每個條目的值替換為在該條目上調用給定函數的結果,直到處理完所有條目或函數引發異常。 |
從接口 java.util.Map 繼承的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Map clear() | 從此映射中刪除所有映射(可選操作)。 |
| Map containsKey() | 如果此映射包含指定鍵的映射,則返回 true。 |
| Map containsValue() | 如果此映射將一個或多個鍵映射到指定值,則返回 true。 |
| entry(K k, V v) | 返回包含給定鍵和值的不可變 Map.Entry。 |
| Map entrySet() | 返回此映射中包含的映射的集合視圖。 |
| Map equals() | 比較指定對象與此映射是否相等。 |
| Map get() | 返回指定鍵映射到的值,如果此映射不包含該鍵的映射,則返回 null。 |
| Map hashCode() | 返回此映射的哈希代碼值。 |
| Map isEmpty() | 如果此映射不包含鍵值映射,則返回 true。 |
| Map keySet() | 返回此映射中包含的鍵的集合視圖。 |
| of() | 返回包含零映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1) | 返回包含單個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2) | 返回包含兩個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3) | 返回包含三個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4) | 返回包含四個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5) | 返回包含五個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5, K k6, V v6) | 返回包含六個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5, K k6, V v6, K k7, V v7) | 返回包含七個映射的不可變映射。 |
| of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5, K k6, V v6, K k7, V v7, K k8, V v8) | 返回包含八個映射的不可變映射。 |
| 的 (K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5, K k6, V v6, K k7, V v7, K k8, V v8, K k9、V v9) | 返回包含九個映射的不可變映射。 |
| 的 (K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5, K k6, V v6, K k7, V v7, K k8, V v8, K k9、V v9、K k10、V v10) | 返回一個包含十個映射的不可變映射。 |
| ofEntries(Map.Entry<? 擴展 K,? 擴展 V>... 條目) | 返回一個不可變映射,其中包含從給定條目中提取的鍵和值。 |
| Map put() | 將指定值與此映射中的指定鍵相關聯(可選操作)。 |
| Map putAll() | 將指定映射中的所有映射複製到此映射(可選操作)。 |
| Map remove() | 從此映射中刪除鍵的映射(如果存在)(可選操作)。 |
| size() | 返回此映射中鍵值映射的數量。 |
| values() | 返回此映射中包含的值的集合視圖。 |
參考:https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/util/concurrent/ConcurrentMap.html
相關用法
- Java ConcurrentModificationException用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap computeIfPresent()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap equals()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap forEach()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap getOrDefault()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap hashcode()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap mappingCount()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap merge()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap newKeySet()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap replace()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap toString()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedQueue forEach()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedQueue removeAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedQueue removeIf()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedQueue retainAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap contains()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap containsKey()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap containsValue()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap elements()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap entrySet()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap get()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap isEmpty()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap keys()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap keySet()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentHashMap put()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自bishaldubey大神的英文原創作品 ConcurrentMap Interface in java。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
