ConcurrentLinkedDequeJava 中的類是Java集合框架並實施采集接口和AbstractCollection 類。它屬於java.util.concurrent包。它用於實現雙端隊列借助LinkedList同時。
ConcurrentLinkedDeque的特點
- 迭代器和分裂器是弱一致的。
- 並發插入、刪除和訪問操作可以跨多個線程安全地執行。
- 它不允許空元素。
- size()方法不是在恒定時間內實現的。由於這些雙端隊列的異步性質,確定當前元素數量需要遍曆元素。
Java 中的 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類是 Deque 接口的線程安全實現,它使用鏈表來存儲其元素。 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類提供了 ArrayDeque 類的可擴展且高性能的替代方案,特別是在多個線程同時訪問雙端隊列的情況下。 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類提供了從雙端隊列兩端插入和刪除元素的方法,以及從雙端隊列的頭部和尾部檢索元素的方法,使其成為需要執行大量添加和刪除操作的場景的不錯選擇。
以下是如何在 Java 中使用 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 的示例:
Java
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<>();
deque.addFirst(1);
deque.addLast(2);
int first = deque.pollFirst();
int last = deque.pollLast();
System.out.println("First: " + first + ", Last: " + last);
}
}First: 1, Last: 2
使用ConcurrentLinkedDeque的優點:
- 線程安全:ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類是線程安全的,這意味著多個線程可以同時訪問它,而不會遇到數據損壞。
- 高效:ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類為從雙端隊列兩端插入和刪除元素提供了恒定時間性能,使其成為需要執行大量添加和刪除操作的場景的不錯選擇。
- 可擴展:ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類使用鏈表來存儲其元素,這使其具有可擴展性,適合在高性能和並發應用程序中使用。
- 高並發:ConcurrentLinkedDeque類使用lock-free算法,這意味著多個線程可以同時訪問雙端隊列,無需加鎖,適合高並發應用。
使用ConcurrentLinkedDeque的缺點:
- 更多內存開銷:ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類使用鏈表來存儲其元素,這意味著它比基於數組的實現(例如 ArrayDeque 類)需要更多內存開銷。
- 容量有限:ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類沒有容量限製,但它仍然需要內存來存儲其元素,這意味著當舊的ConcurrentLinkedDeque 消耗過多內存時,您可能需要創建一個新的ConcurrentLinkedDeque。
類層次結構:
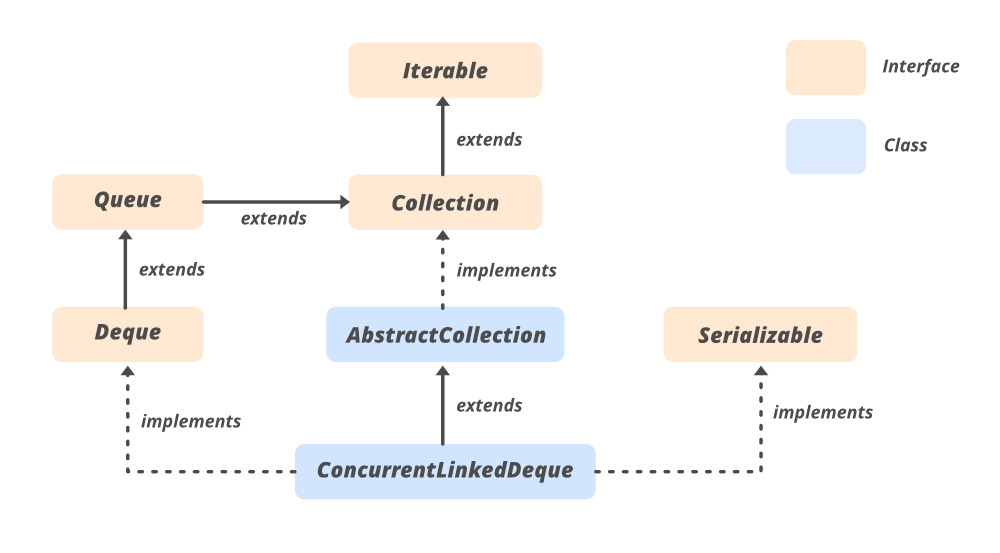
聲明:
public abstract class ConcurrentLinkedDeque<E>
extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Deque<E>, Serializable
Here, E is the type of elements maintained by this collection.
它實現了 Serialized、Iterable
ConcurrentLinkedDeque 的構造函數:
1.ConcurrentLinkedDeque():該構造函數用於構造一個空雙端隊列。
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<E> cld = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<E>();
2. ConcurrentLinkedDeque(Collection<E> c):該構造函數用於構造一個雙端隊列,並將 Collection 的元素作為參數傳遞。
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<E> cld = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<E>(Collection<E> c);
下麵是用Java來說明ConcurrentLinkedDeque的示例程序:
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate ConcurrentLinkedDeque
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentLinkedDequeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedDeque
// using ConcurrentLinkedDeque()
// constructor
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>
cld = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>();
// add element to the front
// using addFirst() method
cld.addFirst(12);
cld.addFirst(70);
cld.addFirst(1009);
cld.addFirst(475);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedDeque: "
+ cld);
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedDeque
// using ConcurrentLinkedDeque(Collection c)
// constructor
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>
cld1 = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>(cld);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedDeque1: "
+ cld1);
}
}ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [475, 1009, 70, 12] ConcurrentLinkedDeque1: [475, 1009, 70, 12]
例子:
Java
// Java code to illustrate
// methods of ConcurrentLinkedDeque
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class ConcurrentLinkedDequeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedDeque
// using ConcurrentLinkedDeque() constructor
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>
cld = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>();
// add element to the front
// using addFirst() method
cld.addFirst(12);
cld.addFirst(70);
cld.addFirst(1009);
cld.addFirst(475);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedDeque: "
+ cld);
// Displaying the Last element
// using getLast() method
System.out.println("The Last element is: "
+ cld.getLast());
// Displaying the first element
// using peekFirst() method
System.out.println("First Element is: "
+ cld.peekFirst());
// Remove the Last element
// using removeLast() method
cld.removeLast();
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedDeque: "
+ cld);
}
}ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [475, 1009, 70, 12] The Last element is: 12 First Element is: 475 ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [475, 1009, 70]
ConcurrentLinkedDeque的基本操作
1. 添加元素
要添加元素或元素集合,ConcurrentLinkedDeque 提供了 add(E e)、addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)、addFirst(E e)、addLast(E e) 等方法。下麵的示例解釋了這些方法。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate adding
// elements to the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AddingElements {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create instance using ConcurrentLinkedDeque
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer> cld1
= new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>();
// Add element to the tail using
// add or addLast methods
cld1.add(12);
cld1.add(110);
// Add element to the head
// using addFirst method
cld1.addFirst(55);
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("Initial Elements in "
+ "the LinkedDeque cld : "
+ cld1);
// create instance using ConcurrentLinkedDeque
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer> cld2
= new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>();
// Add elements of cld1 to the
// cld2 using addAll method
cld2.addAll(cld1);
// Displaying the modified ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("Initial Elements in "
+ "the LinkedDeque cld2: "
+ cld2);
}
}Initial Elements in the LinkedDeque cld : [55, 12, 110] Initial Elements in the LinkedDeque cld2: [55, 12, 110]
輸出:
Initial Elements in the LinkedDeque cld : [55, 12, 110] Initial Elements in the LinkedDeque cld2: [55, 12, 110]
2. 刪除元素
為了刪除元素,ConcurrentLinkedDeque 提供了諸如 remove()、remove(Object o)、removeFirst()、removeLast() 等方法。這些方法在下麵的示例中進行了解釋。
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate removing
// elements of ConcurrentLinkedDeque
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class RemovingElements {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a ConcurrentLinkedDeque
// using ConcurrentLinkedDeque() constructor
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer> cld
= new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<Integer>();
// Add elements using add() method
cld.add(40);
cld.add(50);
cld.add(60);
cld.add(70);
cld.add(80);
// Displaying the existing LinkedDeque
System.out.println(
"Existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque: " + cld);
// remove method removes the first
// element of ConcurrentLinkedDeque
// using remove() method
System.out.println("Element removed: "
+ cld.remove());
// Remove 60 using remove(Object)
System.out.println("60 removed: " + cld.remove(60));
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println(
"Modified ConcurrentLinkedDeque: " + cld);
// Remove the first element
cld.removeFirst();
// Remove the Last element
cld.removeLast();
// Displaying the existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println(
"Modified ConcurrentLinkedDeque: " + cld);
}
}Existing ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [40, 50, 60, 70, 80] Element removed: 40 60 removed: true Modified ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [50, 70, 80] Modified ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [70]
3. 迭代元素
我們可以使用 iterator() 或 descendingIterator() 方法迭代 ConcurrentLinkedDeque。下麵的代碼解釋了這兩種方法。
Java
// Java code to illustrate iterating
// elements of ConcurrentLinkedDeque
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingConcurrentLinkedDeque {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty ConcurrentLinkedDeque
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<String> deque
= new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<String>();
// Use add() method to add elements
// into the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
deque.add("Welcome");
deque.add("To");
deque.add("Geeks");
deque.add("4");
deque.add("Geeks");
// Displaying the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("ConcurrentLinkedDeque: "
+ deque);
// Creating an iterator
Iterator fitr = deque.iterator();
// Displaying the values
// after iterating through the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("The iterator values are: ");
while (fitr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(fitr.next());
}
// Creating a desc_iterator
Iterator ditr = deque.descendingIterator();
// Displaying the values after iterating
// through the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
// in reverse order
System.out.println("The iterator values are: ");
while (ditr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(ditr.next());
}
}
}ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [Welcome, To, Geeks, 4, Geeks] The iterator values are: Welcome To Geeks 4 Geeks The iterator values are: Geeks 4 Geeks To Welcome
4. 訪問元素
為了訪問ConcurrentLinkedDeque的元素,它提供了getFirst()、getLast()、element()等方法。下麵的示例解釋了這些方法。
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate accessing
// elements of ConcurrentLinkedDeque
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
class Accessing {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty ConcurrentLinkedDeque
ConcurrentLinkedDeque<String> cld
= new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<String>();
// Add elements into the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
cld.add("Welcome");
cld.add("To");
cld.add("Geeks");
cld.add("4");
cld.add("Geeks");
// Displaying the ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("Elements in the ConcurrentLinkedDeque: " + cld);
// Displaying the first element
System.out.println("The first element is: "
+ cld.getFirst());
// Displaying the Last element
System.out.println("The Last element is: "
+ cld.getLast());
// Displaying the head of ConcurrentLinkedDeque
System.out.println("The Head of ConcurrentLinkedDeque is: "
+ cld.element());
}
}Elements in the ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [Welcome, To, Geeks, 4, Geeks] The first element is: Welcome The Last element is: Geeks The Head of ConcurrentLinkedDeque is: Welcome
輸出:
Elements in the ConcurrentLinkedDeque: [Welcome, To, Geeks, 4, Geeks] The first element is: Welcome The Last element is: Geeks The Head of ConcurrentLinkedDeque is: Welcome
ConcurrentLinkedDeque的方法
這裏,E是元素的類型。
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque add() | 在此雙端隊列的尾部插入指定元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque addAll() | 將指定集合中的所有元素按照指定集合的迭代器返回的順序附加到此雙端隊列的末尾。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque addFirst() | 在此雙端隊列的前麵插入指定的元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque addLast() | 在此雙端隊列的末尾插入指定的元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque clear() | 從此雙端隊列中刪除所有元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque contains() | 如果此雙端隊列包含指定元素,則返回 true。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque descendingIterator() | 按相反順序返回此雙端隊列中元素的迭代器。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque element() | 檢索但不刪除此雙端隊列表示的隊列頭(換句話說,此雙端隊列的第一個元素)。 |
| forEach(消費者<? super E> 操作) | 對 Iterable 的每個元素執行給定的操作,直到處理完所有元素或該操作引發異常。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque getFirst() | 檢索但不刪除此雙端隊列的第一個元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque getLast() | 檢索但不刪除此雙端隊列的最後一個元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque isEmpty() | 如果此集合不包含任何元素,則返回 true。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque iterator() | 以正確的順序返回此雙端隊列中元素的迭代器。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque offer() | 在此雙端隊列的尾部插入指定元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque offerFirst() | 在此雙端隊列的前麵插入指定的元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque offerLast() | 在此雙端隊列的末尾插入指定的元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque pop() | 從此雙端隊列表示的堆棧中彈出一個元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque push() | 如果可以立即執行此操作而不違反容量限製,則將元素推送到此雙端隊列表示的堆棧上(換句話說,在此雙端隊列的頭部),如果當前沒有可用空間,則拋出 IllegalStateException。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque remove() | 檢索並刪除此雙端隊列所表示的隊列的頭部(換句話說,此雙端隊列的第一個元素)。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque remove() | 從此雙端隊列中刪除第一次出現的指定元素。 |
| 移除全部(集合<?> c) | 刪除指定集合中也包含的所有該集合的元素(可選操作)。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque removeFirst() | 檢索並刪除此雙端隊列的第一個元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque removeFirstOccurrence() | 從此雙端隊列中刪除第一次出現的指定元素。 |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> 過濾器) | 刪除此集合中滿足給定謂詞的所有元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque removeLast() | 檢索並刪除此雙端隊列的最後一個元素。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque removeLastOccurrence() | 從此雙端隊列中刪除最後一次出現的指定元素。 |
| keepAll(集合<?> c) | 僅保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可選操作)。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque size() | 返回此雙端隊列中的元素數量。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque Spliterator() | 返回此雙端隊列中元素的 Spliterator。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque toArray() | 返回一個數組,其中包含此雙端隊列中的所有元素,按正確的順序(從第一個元素到最後一個元素)。 |
| ConcurrentLinkedDeque toArray() | 返回一個數組,其中包含此雙端隊列中的所有元素,按正確的順序(從第一個元素到最後一個元素);返回數組的運行時類型是指定數組的運行時類型。 |
類 java.util.AbstractCollection 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| AbstractCollection containsAll() | 如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,則返回 true。 |
| AbstractCollection toString() | 返回此集合的字符串表示形式。 |
接口 java.util.Collection 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| containsAll(集合<?> c) | 如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,則返回 true。 |
| equals(Object o) | 比較指定對象與此集合是否相等。 |
| hashCode() | 返回此集合的哈希碼值。 |
| parallelStream() | 返回一個可能並行的 Stream 並以此集合作為其源。 |
| stream() | 返回以此集合作為源的順序 Stream。 |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> 生成器) | 返回一個包含此集合中所有元素的數組,使用提供的生成器函數分配返回的數組。 |
接口 java.util.Deque 中聲明的方法
|
METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| peek() | 檢索但不刪除此雙端隊列表示的隊列頭(換句話說,此雙端隊列的第一個元素),或者如果此雙端隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
| peekFirst() | 檢索但不刪除此雙端隊列的第一個元素,或者如果此雙端隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
| peekLast() | 檢索但不刪除此雙端隊列的最後一個元素,或者如果此雙端隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
| poll() | 檢索並刪除此雙端隊列所表示的隊列的頭部(換句話說,此雙端隊列的第一個元素),或者如果此雙端隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
| pollFirst() | 檢索並刪除此雙端隊列的第一個元素,如果此雙端隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
| pollLast() | 檢索並刪除此雙端隊列的最後一個元素,或者如果此雙端隊列為空,則返回 null。 |
參考書:
Brian Goetz、Tim Peierls、Joshua Bloch、Joseph Bowbeer、David Holmes 和 Doug Lea 撰寫的《Java 並發實踐》是 Java 並發編程的綜合指南,包括 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類。本書涵蓋了並發編程的基礎知識,解釋了如何使用java.util.concurrent包,並提供了編寫正確高效代碼的技巧和最佳實踐。如果您想了解有關 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 類和並發編程的更多信息,這本書是一個很好的資源。
相關用法
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque add()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque addAll()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque addFirst()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque addLast()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque clear()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque contains()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque descendingIterator()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque element()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque equals()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque getFirst()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque getLast()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque hashCode()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque isEmpty()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque iterator()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque offer()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque offerFirst()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque offerLast()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque peek()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque peekFirst()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque peekLast()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque poll()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque pollFirst()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque pollLast()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque pop()用法及代碼示例
- Java ConcurrentLinkedDeque push()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自RishabhPrabhu大神的英文原創作品 ConcurrentLinkedDeque in Java with Examples。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
