C 中的 fflush() 函數
原型:
int fflush(FILE *filename);
參數:
FILE *filename
返回類型:0 或 EOF
函數的使用:
當我們處理文件處理時,我們處理流而不是處理文件。有三種類型的流stdin(標準輸入),stderr(標準誤差),stdout(標準輸出)。 fflush() 函數用於在程序每次迭代後刷新緩衝區。當我們打開一個文件進行寫入操作時,調用 fflush() 函數有助於寫入文件並清除流中的緩衝區。 ffiush()函數的原型是:int fflush(FILE* filename);
返回值零表示成功,返回值 EOF 表示發生了一些錯誤。
C 中的 fflush() 示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
//Initialize the file pointer
FILE* f;
//Take a array of characters
char ch[100];
//Create the file for write operation
f = fopen("includehelp.txt", "w");
printf("Enter five strings\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//take the strings from the users
scanf("%[^\n]", &ch);
//write back to the file
fputs(ch, f);
//every time take a new line for the new entry string
fputs("\n", f);
//except for last entry.Otherwise print the last line twice
//clear the stdin stream buffer
//fflush(stdin);
//if we don't write this then after taking string
//%[^\n] is waiting for the '\n' or white space
}
//take the strings from the users
scanf("%[^\n]", &ch);
fputs(ch, f);
//close the file after write operation is over
fclose(f);
//open a file
f = fopen("includehelp.txt", "r");
printf("File content is--\n");
printf("\n...............print the strings..............\n");
while (!feof(f)) {
//takes the first 100 character in the character array
fgets(ch, 100, f);
//and print the strings
printf("%s", ch);
}
//close the file
fclose(f);
return 0;
}輸出
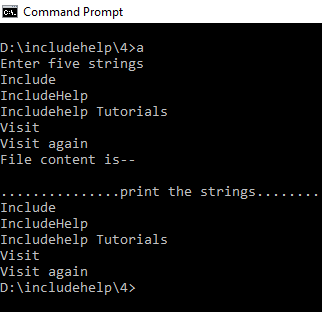
如果我們這裏不使用 fflush() 函數。然後輸出將是...
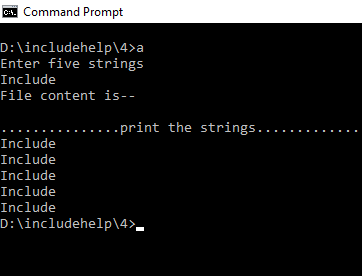
相關用法
- C語言 fread()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 feof()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fillellipse()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fgets()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 freopen()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 frexp()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fclose()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fseek() vs rewind()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fgetc()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fputc()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fputs()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fillpoly()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 ftell()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fseek()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fgets() and gets()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fscanf()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 ferror()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fgetc() and fputc()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fwrite()用法及代碼示例
- C語言 fork()用法及代碼示例
注:本文由純淨天空篩選整理自Souvik Saha大神的英文原創作品 fflush() function in C language with Example。非經特殊聲明,原始代碼版權歸原作者所有,本譯文未經允許或授權,請勿轉載或複製。
